 Meles meles
Meles meles
-----------
English: Badger
German: Dachs
French: Blaireau
Spanish: Tejon
Distribution areas
------------------
The badger is found throughout Europe
and Asia with the exception of the most
northern areas. In many regions this animal
in now very scarce, so it is regarded as a
species in danger of extinction.
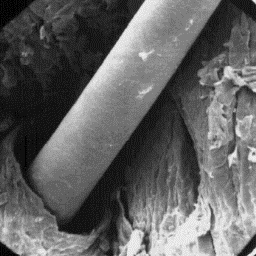
Description of the fur The surface structure
---------------------- of the skin, 200x
The skins are from 60 to 75 cm long. The
fur coat consists of long, dark-brown coarse fibres and a lightly coloured
undercoat layer about 20 mm thick. The length of the guard hairs is between
45 and 60 mm. The head is white but has two black stripes on the sides, which
become larger and disappear at the neck.
|
|
 Meles meles
Meles meles
-----------
English: Badger
German: Dachs
French: Blaireau
Spanish: Tejon
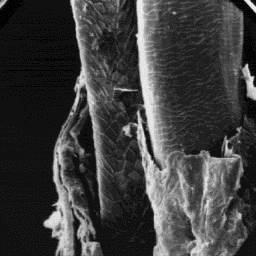
Structure of the hair
---------------------
The microscopic structure of the skin
surface is furrowed and the hair follicles
are narrow, with the inner sheath
protruding. The average follicle contains
two hair shafts.
The fine fur fibres are circular and, in The cuticular structure
the upper parts of the shaft, also of a guard hair, 200x
ellipsoidal in cross section. The diameter
is in the range of 30 to 90 µm. The cuticular scales are even tile-like with
a smooth surface and straight scale margins. These fine fur fibres are
usually non-medullated.
|
|
 Meles meles
Meles meles
-----------
English: Badger
German: Dachs
French: Blaireau
Spanish: Tejon
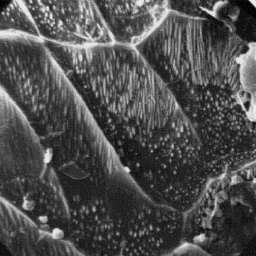
The cross-sectional outline of the inter-
mediate fibres is circular at the bottom,
and ellipsoidal in the middle and upper
parts, of the shafts. The diameter of these
fibres is from 90 to 120 µm and the
cuticular scales are even tile-like in
shape with a non-regular type, with
non-uniform cavities of variable size and
shape, and with a foam-like and amorphous The cuticular structure
infilling material. of a guard hair, 2000x
The guard hairs are ellipsoidal, but, at the bottom, circular, in
cross-sectional outline. Their diameter is in the range of 100 and 250 µm.
The cuticular scales are even tile-like and, in the upper part of the shaft,
usually crenated tile-like in shape. The scale surface is smooth or
non-regular grooved and the scale margins are straight, with exception of the
upper parts of the shaft, where they are rippled.
|
|
 Meles meles
Meles meles
-----------
English: Badger
German: Dachs
French: Blaireau
Spanish: Tejon
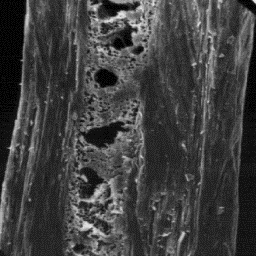
The medulla is narrow, central sym-
metrical-shaped in cross-section and
longitudinally unbroken. The overall medul-
lar structure belongs to the non-regular
type, with an amorphous and sometimes foam-
-like infilling material.
Longitudinal section
of an intermediate fibre, 600x
|
|
 Meles meles
Meles meles
-----------
English: Badger
German: Dachs
French: Blaireau
Spanish: Tejon
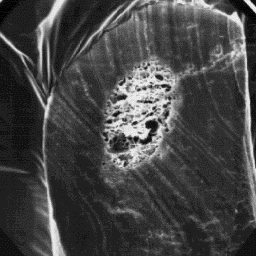
Transverse section
of an intermediate fibre, 400x
Numerical code for badger skin structure
----------------------------------------
Surface of the skin: 3-6-2
Fine fur fibres: 2.1-2-1-1-4-0-0-0-0-30.91-8.28
Intermediate fibres: 2.1-2-3-1-3-1-1-16-6.8-90.121-20.45
Guard hairs: 2.1-2.4-1.3-1.2-3-1-1-16-6.8-100.251-30.61
|




